Gut Health: How the Gut-Brain Connection Affects Your Overall Well-Being
September 22, 2023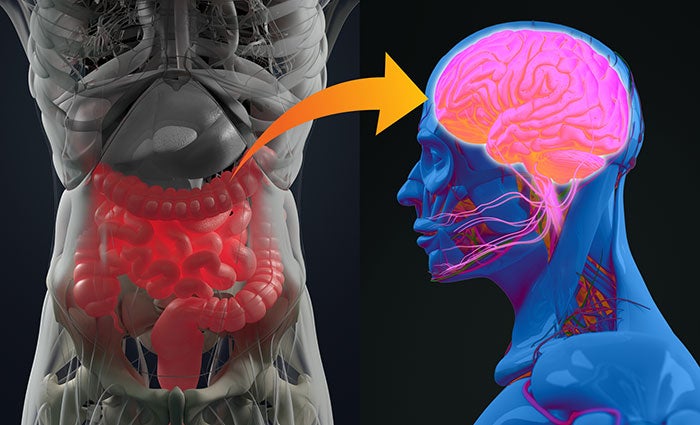
Categories: Blog Posts
Did you know that your gut health has a significant impact on more than just your digestion?
Gut Health: How the Gut-Brain Connection Affects Your Overall Well-Being
Did you know that your gut health has a significant impact on more than just your digestion? Let’s take a closer look at the importance of gut health and its surprising connection with your brain, and your overall well-being.
Understanding the Gut Microbiota:
- At the heart of our digestive system lies a bustling ecosystem of microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota. This intricate community, comprised of trillions of diverse microbial inhabitants, activates biological processes that profoundly impact our well-being. The microbiota aids digestion, supports nutrient absorption, and fortifies our immune defense. Aside from assisting with these vital processes, the gut also has an interesting connection to our brains.
The Gut-Brain Connection:
- The gut-brain connection, also known as the gut-brain axis, refers to the two-way communication system that exists between the gastrointestinal tract (the gut) and the central nervous system (the brain). This communication network involves complex interactions between neural, hormonal, and immune pathways, allowing information to flow between the gut and the brain.
The gut communicates with the brain through various channels, including the vagus nerve, which directly connects the gut to the brainstem. Additionally, the gut produces a wide range of molecules, such as neurotransmitters and hormones, that can influence brain function and behavior.
As the brain communicates with the gut, it influences its function and activity. Emotional and psychological factors, such as stress and anxiety, can impact gut motility, secretion of digestive enzymes, and the composition of the gut microbiota—those microorganisms residing in the gut.
The gut-brain connection means that our mood and cognitive function isn’t all in our head, it’s also affected by our gut, just as digestion isn’t solely a gut decision. Further, research suggests that imbalances in the gut microbiota can be associated with conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), depression, and anxiety.
How Does Poor Gut Health Affect Your Mental Health?
- Mood Disorders: Imbalances in the gut microbiota can impact the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a crucial role in regulating mood. Disrupted levels of these neurotransmitters due to poor gut health are associated with an increased risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Inflammation and Cognitive Function: Unhealthy gut conditions can trigger chronic inflammation and activate the body's stress response. This inflammation can extend to the brain, contributing to cognitive problems and impairing memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities.
- Stress Response Dysregulation: A compromised gut-brain axis can lead to a dysregulated stress response. Chronic stress, influenced by poor gut health, can aggravate mental health issues. Likewise, elevated stress levels can further disrupt gut health, creating a vicious cycle that affects both mental and gut well-being.
Five Actions to Achieve and Maintain a Healthier Gut
- Choose a Balanced Diet: Consume a diverse range of whole foods, including fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. These foods support a healthy gut microbiota by providing essential nutrients and promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria.
- Add in Probiotics and Fermented Foods: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha into your diet. These foods introduce beneficial live bacteria to your gut, promoting microbial diversity and balance.
- Select Prebiotic Foods: Include prebiotic-rich foods such as garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus. Prebiotics serve as nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria, helping them flourish and maintain a healthy gut environment.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water daily to support digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut function. Proper hydration helps maintain the mucosal lining of the gut, which is essential for a healthy digestive system. A simple rule to follow is to take your total weight and divide that number in half. That's how many ounces of water you should drink per day. For instance, a person who is 200 pounds should drink 100 oz of water per day.
- Manage Stress: Engage in stress-reducing practices such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or regular physical activity. Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health, so managing stress is vital for maintaining a balanced gut-brain axis.
Conclusion: Your gut health is far more than just digestion – it's a complex ecosystem that influences your overall well-being, from your physical health to your mood. By nurturing a diverse and balanced gut microbiota through your diet and lifestyle choices, you can take significant steps toward promoting not only digestive health but also a healthier brain and body.
If you have specific gut-related concerns or health conditions, consult your physician or seek out a Mount Carmel healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
